
ZhETF, Vol. 168,
No. 3,
p. 414 (September 2025)
(English translation - JETP,
Vol. 141, No. 3,
September 2025
available online at www.springer.com
)
Stabilization of the Collinear Plateau Phase by Thermal Fluctuations in the Diluted Triangular Lattice Antiferromagnet Rb(1-x)KxFe(MoO4)2
Glazkov V.N., Krastilevskiy I.A.
Received: July 25, 2025
DOI: 10.7868/S3034641X25100144
The triangular lattice antiferromagnet RbFe(MoO4)2 orders antiferromagnetically in a planar 120 -structure below -structure below 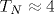 K. A striking feature of RbFe(MoO4)2 magnetic phase diagram is the presence of collinear «1/3-plateau» magnetic phase, which is stabilized by thermal and quantum fluctuations at magnetic fields in the vicinity of 1/3 of a saturation field. Quenched disorder caused by impurities is predicted to act against the effect of fluctuations and to suppress collinear plateau phase [V. S. Maryasin and M. E. Zhitomirsky, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 247201 (2013)]. Balance between «dynamic» thermal and quantum fluctuations and «static» impurity-induced disorder is temperature-sensitive, which allows thermal fluctuations to take over the effect of static disorder and leads to the restoration of the fluctuation-stabilized «1/3-plateau» phase on heating. Here we present experimental results directly confirming this prediction and demonstrating re-establishment of the plateau-like phase in the diluted Rb(1-x)KxFe(MoO4)2 sample at moderate dilution level x=0.15 on increasing the temperature. K. A striking feature of RbFe(MoO4)2 magnetic phase diagram is the presence of collinear «1/3-plateau» magnetic phase, which is stabilized by thermal and quantum fluctuations at magnetic fields in the vicinity of 1/3 of a saturation field. Quenched disorder caused by impurities is predicted to act against the effect of fluctuations and to suppress collinear plateau phase [V. S. Maryasin and M. E. Zhitomirsky, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 247201 (2013)]. Balance between «dynamic» thermal and quantum fluctuations and «static» impurity-induced disorder is temperature-sensitive, which allows thermal fluctuations to take over the effect of static disorder and leads to the restoration of the fluctuation-stabilized «1/3-plateau» phase on heating. Here we present experimental results directly confirming this prediction and demonstrating re-establishment of the plateau-like phase in the diluted Rb(1-x)KxFe(MoO4)2 sample at moderate dilution level x=0.15 on increasing the temperature.
|
|