
ZhETF, Vol. 133,
No. 1,
p. 80 (January 2008)
(English translation - JETP,
Vol. 106, No. 1,
January 2008
available online at www.springer.com
)
ATMOSPHERIC GAMMA-RAY AND NEUTRON FLASHES
Babich L.P., Kudryavtsev A.Yu., Kudryavtseva M.L., Kutsyk I.M.
Received: May 3, 2007
PACS: 92.60.Pw, 52.80.Mg
Gamma-ray pulses are calculated from 2D numerical simulations of the upward atmospheric discharge in a selfconsistent electric field using the multi-group approach to the kinetics of relativistic runaway electrons (REs). Computed γ-ray numbers and spectra are consistent with those of terrestrial γ-ray flashes (TGFs) observed aboard spacecrafts. The RE flux is concentrated mainly within the domain of the Blue Jet fluorescence. This confirms that exactly the domain adjacent to a thundercloud is the source of the observed γ-ray flashes. The yield of photonuclear neutrons is calculated. One γ-ray pulse generates 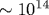 -1015 neutrons. The possibility of direct deposition of REs to the detector readings and the origin of the lightning-advanced TGFs are discussed. -1015 neutrons. The possibility of direct deposition of REs to the detector readings and the origin of the lightning-advanced TGFs are discussed.
|
|