
ZhETF, Vol. 133,
No. 1,
p. 162 (January 2008)
(English translation - JETP,
Vol. 106, No. 1,
January 2008
available online at www.springer.com
)
FLEXIBLE-TO-SEMIFLEXIBLE CHAIN CROSSOVER ON THE PRESSURE-AREA ISOTHERM OF A LIPID BILAYER
Krivonos I.N., Mukhin S.I.
Received: June 11, 2007
PACS: 87.16.Dg, 87.15.Kg, 31.15.Kb
We find theoretically that competition between 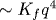 and and 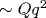 terms in the Fourier-transformed conformational energy of a single lipid chain, in combination with interchain entropic repulsion in the hydrophobic part of the lipid (bi)layer, may cause a crossover on the bilayer pressure-area isotherm terms in the Fourier-transformed conformational energy of a single lipid chain, in combination with interchain entropic repulsion in the hydrophobic part of the lipid (bi)layer, may cause a crossover on the bilayer pressure-area isotherm 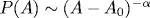 . The crossover manifests itself in the transition from α=5/3 to α=3. Our microscopic model represents a single lipid molecule as a worm-like chain with a finite irreducible cross-section area A0, a flexural rigidity Kf, and a stretching modulus Q in a parabolic potential with the self-consistent curvature B(A) formed by entropic interactions between hydrocarbon chains in the lipid layer. The crossover area A* obeys the relation . The crossover manifests itself in the transition from α=5/3 to α=3. Our microscopic model represents a single lipid molecule as a worm-like chain with a finite irreducible cross-section area A0, a flexural rigidity Kf, and a stretching modulus Q in a parabolic potential with the self-consistent curvature B(A) formed by entropic interactions between hydrocarbon chains in the lipid layer. The crossover area A* obeys the relation 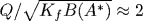 . We predict a peculiar possibility of deducing the effective elastic moduli Kf and Q of an individual hydrocarbon chain from the analysis of the isotherm with such a crossover. Also calculated is crossover-related behavior of the area compressibility modulus KA, the equilibrium area per lipid At, and the chain order parameter S(θ). . We predict a peculiar possibility of deducing the effective elastic moduli Kf and Q of an individual hydrocarbon chain from the analysis of the isotherm with such a crossover. Also calculated is crossover-related behavior of the area compressibility modulus KA, the equilibrium area per lipid At, and the chain order parameter S(θ).
|
|