
ZhETF, Vol. 124,
No. 1,
p. 48 (July 2003)
(English translation - JETP,
Vol. 97, No. 1,
p. 42,
July 2003
available online at www.springer.com
)
DISTRIBUTION AND EVOLUTION OF ELECTRONS IN A CLUSTER PLASMA CREATED BY A LASER PULSE
Smirnov M.B.
Received: January 30, 2003
PACS: 36.40.Wa, 33.90.+h
We analyze the properties and the character of evolution of the electron subsystem of a large cluster (with the number of atoms 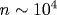 -106) interacting with a short laser pulse of high intensity (1017-1019 W/cm2). As a result of ionization in a strong laser field, cluster atoms are converted into multicharged ions, a part of forming electrons leaves the cluster, and the other electrons move in a self-consistent field of the charged cluster and the laser wave. It is shown that electron-electron collisions are inessential both during the cluster irradiation by the laser pulse and in the course of cluster expansion; the electron distribution in the cluster does not therefore transform into the Maxwell one even during the cluster expansion. During the cluster expansion, the Coulomb field of a cluster charge acts on cluster ions stronger than the pressure resulting from electron-ion collisions. In addition, bound electrons remain inside the cluster in the course of its expansion, and cluster expansion does not therefore lead to additional cluster ionization. -106) interacting with a short laser pulse of high intensity (1017-1019 W/cm2). As a result of ionization in a strong laser field, cluster atoms are converted into multicharged ions, a part of forming electrons leaves the cluster, and the other electrons move in a self-consistent field of the charged cluster and the laser wave. It is shown that electron-electron collisions are inessential both during the cluster irradiation by the laser pulse and in the course of cluster expansion; the electron distribution in the cluster does not therefore transform into the Maxwell one even during the cluster expansion. During the cluster expansion, the Coulomb field of a cluster charge acts on cluster ions stronger than the pressure resulting from electron-ion collisions. In addition, bound electrons remain inside the cluster in the course of its expansion, and cluster expansion does not therefore lead to additional cluster ionization.
|
|