
ZhETF, Vol. 123,
No. 1,
p. 137 (January 2003)
(English translation - JETP,
Vol. 96, No. 1,
p. 118,
January 2003
available online at www.springer.com
)
RECONSTRUCTION OF THE 2D HOLE GAS SPECTRUM FOR SELECTIVELY DOPED p-Ge/Ge1-xSix HETEROSTRUCTURES
Arapov Yu.G., Harus G.I., Neverov V.N., Shelushinina N.G., Yakunin M.V., Kuznetsov O.A.
Received: March 20, 2002
PACS: 73.43.-f
The magnetic field (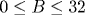 T) and temperature ( T) and temperature (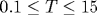 K) dependences of longitudinal and Hall resistivities have been investigated for p-Ge0.93Si0.07/Ge multilayers with different Ge layer widths 12 nm K) dependences of longitudinal and Hall resistivities have been investigated for p-Ge0.93Si0.07/Ge multilayers with different Ge layer widths 12 nm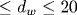 nm and hole densities ps=(1-5)• 1015 m-2. An extremely high sensitivity of the experimental data (the structure of magnetoresistance traces, relative values of the inter-Landau-level gaps deduced from the activation magnetotransport, etc.) to the quantum well profile is revealed in the cases where the Fermi level reaches the second confinement subband. An unusually high density of localized states between the Landau levels is deduced from the data. Two models for the long-range random impurity potential (the model with randomly distributed charged centers located outside the conducting layer and the model of the system with a spacer) are used to evaluate the impurity potential fluctuation characteristics: the random potential amplitude, the nonlinear screening length in the vicinity of integer filling factors
u= 1 and
u=2, and the background density of states (DOS). The described models are suitable for explanation of the observed DOS values, while the short-range impurity potential models fail. For half-integer filling factors, the linear temperature dependence of the effective quantum Hall effect plateau-plateau (PP) transition widths
u0(T) is observed, contrary to the expected scaling behavior of the systems with short-range disorder. The finite nm and hole densities ps=(1-5)• 1015 m-2. An extremely high sensitivity of the experimental data (the structure of magnetoresistance traces, relative values of the inter-Landau-level gaps deduced from the activation magnetotransport, etc.) to the quantum well profile is revealed in the cases where the Fermi level reaches the second confinement subband. An unusually high density of localized states between the Landau levels is deduced from the data. Two models for the long-range random impurity potential (the model with randomly distributed charged centers located outside the conducting layer and the model of the system with a spacer) are used to evaluate the impurity potential fluctuation characteristics: the random potential amplitude, the nonlinear screening length in the vicinity of integer filling factors
u= 1 and
u=2, and the background density of states (DOS). The described models are suitable for explanation of the observed DOS values, while the short-range impurity potential models fail. For half-integer filling factors, the linear temperature dependence of the effective quantum Hall effect plateau-plateau (PP) transition widths
u0(T) is observed, contrary to the expected scaling behavior of the systems with short-range disorder. The finite 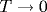 width of the PP transitions may be due to an effective low-temperature screening of a smooth random potential due to the Coulomb repulsion of electrons. width of the PP transitions may be due to an effective low-temperature screening of a smooth random potential due to the Coulomb repulsion of electrons.
|
|