
ZhETF, Vol. 120,
No. 3,
p. 700 (September 2001)
(English translation - JETP,
Vol. 93, No. 3,
p. 615,
September 2001
available online at www.springer.com
)
SUPERCONDUCTIVITY IN Ba1-xKxBiO3: POSSIBLE SCENARIO OF SPATIALLY SEPARATED FERMI-BOSE MIXTURE
Menushenkov A.P., Klementev K.V., Kuznetsov A.V., Kagan M.Yu.
Received: March 16, 2001
PACS: 74.20.Mn, 74.72.Yg
We propose a new scenario for the metal-insulator phase transition and superconductivity in the perovskite-like bismuthates Ba1-xKxBiO3 (BKBO) based on our EXAFS studies. We show that two types of charge carriers, the local pairs (real-space bosons) and the itinerant electrons, exist in the metallic compound Ba1-xKxBiO3 (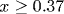 ). The real-space bosons are responsible for the charge transport in semiconducting BaBiO3 and for superconductivity in the metallic BKBO. The appearance of the Fermi-liquid state as the percolation threshold is overcome ( ). The real-space bosons are responsible for the charge transport in semiconducting BaBiO3 and for superconductivity in the metallic BKBO. The appearance of the Fermi-liquid state as the percolation threshold is overcome (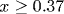 ) explains the observed metal-insulator phase transition. Because bosons and fermions occupy different types of the octahedral BiO6 complexes, they are separated in real space, and therefore, the spatially separated Fermi-Bose mixture of a new type is likely to be realized in the bismuthates. The nature of superconductivity is consistently explained in the framework of this scenario. A new superconducting oxide Ba1-xLaxPbO3 has been successfully synthesized to check our conclusions. ) explains the observed metal-insulator phase transition. Because bosons and fermions occupy different types of the octahedral BiO6 complexes, they are separated in real space, and therefore, the spatially separated Fermi-Bose mixture of a new type is likely to be realized in the bismuthates. The nature of superconductivity is consistently explained in the framework of this scenario. A new superconducting oxide Ba1-xLaxPbO3 has been successfully synthesized to check our conclusions.
|
|