
ZhETF, Vol. 120,
No. 3,
p. 555 (September 2001)
(English translation - JETP,
Vol. 93, No. 3,
p. 485,
September 2001
available online at www.springer.com
)
NUCLEAR FUSION INDUCED BY A SUPER-INTENSE ULTRASHORT LASER PULSE IN THE DEUTERATED GLASS AEROGEL
Krainov V.P., Smirnov M.B.
Received: April 20, 2001
PACS: 52.58.Ns, 52.50.Jm, 52.70.Nc
A SiO2 aerogel with absorbed deuterium is proposed as a target for the fusion reaction 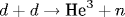 induced by a super-intense ultrashort laser pulse. The multiple inner ionization of oxygen and silicon atoms in the aerogel skeleton occurs in the super-intense laser field. All the forming free electrons are heated and removed from the aerogel skeleton by the laser field at the front edge of the laser pulse. The subsequent Coulomb explosion of the deuterated charged aerogel skeleton propels the deuterium ions up to kinetic energies of ten keV and higher. The neutron yield is estimated up to 105 neutrons per laser pulse during induced by a super-intense ultrashort laser pulse. The multiple inner ionization of oxygen and silicon atoms in the aerogel skeleton occurs in the super-intense laser field. All the forming free electrons are heated and removed from the aerogel skeleton by the laser field at the front edge of the laser pulse. The subsequent Coulomb explosion of the deuterated charged aerogel skeleton propels the deuterium ions up to kinetic energies of ten keV and higher. The neutron yield is estimated up to 105 neutrons per laser pulse during 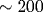 -500 ps if the peak intensity is 1018 W/cm2 and the pulse duration is 35 fs. -500 ps if the peak intensity is 1018 W/cm2 and the pulse duration is 35 fs.
|
|