
ZhETF, Vol. 117,
No. 6,
p. 1198 (June 2000)
(English translation - JETP,
Vol. 90, No. 6,
p. 1042,
June 2000
available online at www.springer.com
)
HIGH-FIELD MAGNETORESISTANCE AND HALL EFFECT IN Bi2Sr2CuOx SINGLE CRYSTALS
Vedeneev S.I., Jansen A.G.M., Wyder P.
Received: December 9, 1999
PACS: 74.25.Fy, 74.62.Dh, 74.72.Hs
We investigated the in-plane magnetoresistance and the Hall effect of high-quality Bi2Sr2CuOx single crystals with Tc(midpoint) =3.7-9.6 K in dc magnetic fields up to 23 T. For T<10 K, the crystals show the classical positive magnetoresistance. Starting from 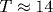 K, an anomalous negative magnetoresistance appears at low magnetic fields; for K, an anomalous negative magnetoresistance appears at low magnetic fields; for  K, the magnetoresistance is negative in the whole studied range of magnetic fields. Temperature and magnetic field dependences of the negative magnetoresistante single crystals are qualitatively consistent with the electron interaction theory developed for simple semiconductors and disorded metals. As observed for other cuprate superconductors, the Hall resistivity is negative in the mixed state and changes its sign with increasing the field. The linear T-dependence of \ctgθ H for the Hall angle in the normal state closely resembles that of the normal-state resistivity as expected for a Fermi-liquid picture. K, the magnetoresistance is negative in the whole studied range of magnetic fields. Temperature and magnetic field dependences of the negative magnetoresistante single crystals are qualitatively consistent with the electron interaction theory developed for simple semiconductors and disorded metals. As observed for other cuprate superconductors, the Hall resistivity is negative in the mixed state and changes its sign with increasing the field. The linear T-dependence of \ctgθ H for the Hall angle in the normal state closely resembles that of the normal-state resistivity as expected for a Fermi-liquid picture.
|
|